How Do Electronics Work? Complete Guide
Published: 25 Nov 2025
Have you ever wondered how your phone, TV, or laptop actually works? Every day, we use these devices without thinking about the magic happening inside them. Understanding how electronics work might sound tricky, but it doesn’t have to be.
In this guide, we will explain how do electronics work in a simple way. You’ll learn how different devices function, the main types of electronics, and some easy tips to get started. This is a perfect beginner-friendly introduction to electronics for beginners, with real-life examples you can relate to.
What Are Electronics?
Electronics are devices that use electricity to do work or control information. Unlike simple electrical devices like bulbs or fans, electronic devices can process and manage information.
For example, your smartphone, TV, and digital watch are all electronic devices. They don’t just use electricity; they perform tasks like showing videos, sending messages, or keeping time.
There are different types of electronics:
- Consumer electronics: Smartphones, laptops, TVs
- Industrial electronics: Factory machines and sensors
- Communication electronics: Radios, Wi-Fi devices
How Do Electronics Work?
Electronics work by controlling the flow of electricity through circuits to perform specific tasks. Understanding this basic principle helps beginners see how devices turn power into actions like sound, light, or motion.
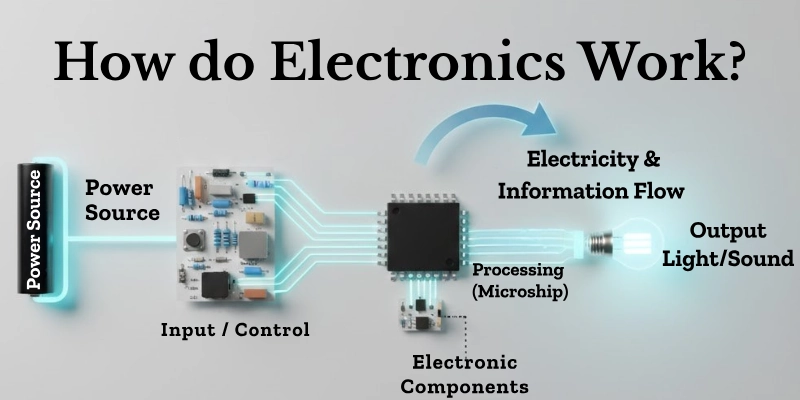
The electronics working principle is simple once you break it down into steps:
- Electricity flows through a circuit:
Electricity moves from the power source through the circuit, passing through components, and finally reaching the output. Think of it as water flowing through pipes to reach a faucet. - Control of current:
Components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors regulate how much electricity flows and when. This keeps the device working safely and correctly. - Processing signals:
Microchips or ICs take the electrical signals and process them. For example, when you press a button, the microchip interprets it and sends a signal to produce the desired action. - Output devices:
The processed signal reaches output devices, which create results like sound, light, or motion. For example, speakers produce sound, LEDs light up, and motors move.
This is the basic idea of how electronic devices work and is a perfect start for anyone learning beginner electronics.
Main Components and Their Functions
Electronics are made up of small parts called basic electronic components, each with a special job. Understanding them helps beginners see how devices work.

- Resistors:
Resistors control the amount of current flowing in a circuit. They prevent too much electricity from damaging other parts. - Capacitors:
Capacitors store and release energy when needed, helping circuits work smoothly. - Diodes:
Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, protecting circuits and controlling electricity flow. - Transistors:
Transistors act as switches or amplifiers, controlling signals and electricity in a circuit. - Integrated Circuits (ICs):
ICs are tiny circuits that perform complex functions in a small package, like running a smartphone or a TV.
| Tip |
|---|
|
Learning the IC working and other components is the first step for understanding more advanced electronics. |
How Circuits Make Electronics Work?
By learning how electronic circuits work, beginners can understand the electronics flow from power → components → sensors → outputs, which is the core working of circuits.
Circuits are the pathways that allow electricity to flow and make electronic devices work.
- Simple circuits:
A basic example is a battery lighting an LED. Electricity flows from the battery through the LED, making it glow. - Complex circuits:
In devices like smartphones, circuits process many inputs at once, such as touch on the screen, and send signals to perform actions. - Sensors and inputs:
Sensors detect signals like touch, light, or motion. These inputs tell the device what to do next. - Outputs:
The processed signals reach outputs like LEDs, sound, motors, or screens, showing the result of the circuit’s work.
Example: Pressing a button on a TV remote sends a signal through the circuit that the TV understands, changing the channel instantly.
Types of Electronics
Electronics are divided into different categories based on their use, called types of electronics. From consumer electronics examples like phones and TVs to embedded electronics in smart appliances, each type has a specific function in daily life.
Here are the main types of electronics:
| Type | Example | Function |
| Consumer Electronics | Phones, laptops, TVs | Used for daily tasks and entertainment |
| Industrial Electronics | Robotics, machines | Help factories and industries operate |
| Communication Electronics | Radios, routers | Transmit and receive information |
| Medical Electronics | Heart monitors, medical devices | Diagnose and monitor health |
| Embedded Electronics | Smart appliances, wearables | Built into devices to perform specific tasks |
Tip: Including a simple table like this makes it easier for beginners to understand consumer electronics examples and embedded electronics at a glance.
Examples of How Electronics Work in Daily Life
Electronics are everywhere, and they make our daily tasks easier. Here are some simple electronics examples showing how they work:
- Smartphone: Touch input → IC processes the signal → Screen updates instantly.
- TV: Remote button pressed → Signal processed by the circuit → Screen changes the channel.
- Smartwatch: Sensor detects heart rate → Microchip calculates the data → Display shows your heartbeat.
- LED light: Electricity flows through a resistor → LED lights up.
These examples show how electronics in daily life use circuits, sensors, and microchips to perform tasks quickly and efficiently. They are perfect real-life electronics that make work, communication, and entertainment easier.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electronics
Electronics have changed our daily lives in many ways, but they also come with some drawbacks. Here’s a simple comparison showing the benefits and drawbacks of electronics:
| Pros | Cons |
| Make communication faster and easier | Can cause addiction or overuse |
| Improve work productivity | Expensive to buy and maintain |
| Provide entertainment and learning tools | May lead to health issues (eye strain, poor posture) |
| Help in healthcare and medical devices | It can be complex to repair or understand |
| Automate tasks and save time | Dependence on electricity and the internet |
Tips for Understanding How Electronics Work
Learning electronics can be fun and easy if you start simple. Here are some practical electronics tips for beginners:
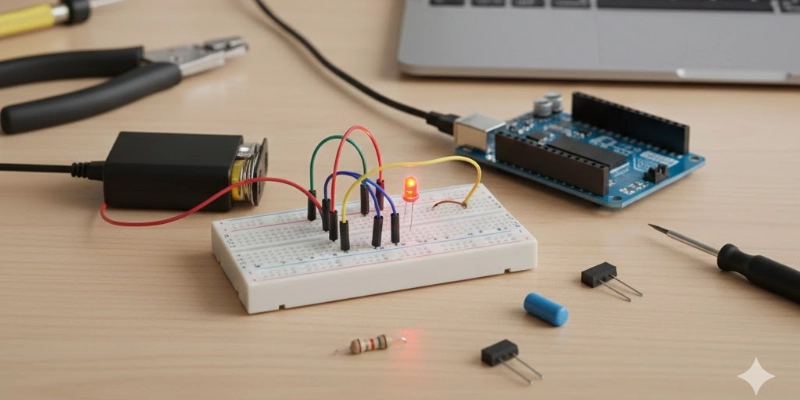
- Start with small circuits: Use simple setups like LEDs, batteries, and switches to see how electricity flows.
- Learn the main components first: Understand parts like resistors, capacitors, and transistors before moving to complex circuits.
- Practice building simple circuits: Use kits like Arduino or Raspberry Pi to get hands-on experience.
- Watch beginner-friendly tutorials: Videos and guides can make learning easier and more visual.
Following these steps is a great way to learn electronics and follow a beginner electronics guide effectively.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about how do electronics work. Electronics work by controlling and processing electricity through components and circuits. Sensors, microchips, and output devices all work together to make devices perform tasks efficiently.
Understanding how electronics function helps us appreciate the devices we use every day, from smartphones and TVs to smart home gadgets. This conclusion on electronics shows that even complex devices follow simple principles that anyone can learn.
FAQs
Want to understand electronics better? Check out our beginner-friendly FAQs!
Electronics work by sending electric signals through small pathways called circuits. Components like transistors and diodes help control these signals. The signals are then used to make devices perform tasks, such as lighting a screen or sending a message.
Yes, even when turned off, many TVs still draw a small amount of power called standby power. This keeps features like remote control sensors active. Although it’s small, it adds up over time if many devices are left plugged in.
The 7 basic digital gates are AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. Each gate performs a simple logic operation on input signals. By combining these gates, computers and other digital devices make decisions and process information.
Electronics covers devices and circuits that control or process electric signals. It includes everything from tiny microchips to large communication systems. Basically, any device that uses electricity to handle information falls under electronics.
Physics explains how electricity moves and how materials respond to it. Concepts like voltage, current, and resistance help design circuits and components. Without physics, we couldn’t predict or control how electronic devices behave.
Yes, many phone chargers use a small amount of electricity even when nothing is plugged in. This is called phantom or standby power. It’s usually very low, but unplugging chargers saves energy over time.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks