Beginner’s Guide to Computer Networking Made Easy
Published: 28 Sep 2025
Have you ever shared files, printed documents, or used the internet on multiple devices? That’s all possible because of computer networking. Simply put, it connects devices so they can share data, resources, and information.
Networking is everywhere, from home Wi-Fi to office systems, making communication faster and work easier.
This article explains computer networking, its types, devices, pros and cons, examples, and common questions.
What is Computer Networking?
Computer networking is the process of connecting two or more computers or devices so they can share data, the internet, and resources like printers or storage devices.
Networking makes it easy to share information, access the internet, communicate quickly, and manage resources efficiently. It is essential for both homes and businesses.
Examples in Daily Life:
Some common examples of computer networking include:
- Home Wi-Fi connects smartphones, laptops, and smart devices.
- Office LANs for sharing files and printers.
- Internet cafes allow multiple users to be online.
- Cloud networks store and access data remotely.
History of Computer Networking
Computer networking began in the 1960s with ARPANET and packet switching. Over time, it evolved through LANs, WANs, Ethernet, and now includes the Internet, Wi-Fi, and cloud computing.
- In the 1960s, ARPANET used packet switching to connect computers and share data over long distances.
- In the 1980s–1990s, Ethernet, LANs, and WANs made connecting multiple computers in offices and schools easier.
- Today, the Internet, Wi-Fi, and cloud computing connect devices worldwide, enabling fast communication and data sharing.
Types of Computer Networks
Computer networks range from small PANs and LANs to city-wide MANs, global WANs, wireless connections, and secure VPNs.
Here are some types of computer networks.
- Personal Area Network (PAN):
A PAN connects devices in a very small area, like a phone, laptop, or tablet, usually within a few meters. - Local Area Network (LAN):
A LAN is a network for a home, office, or school, allowing multiple devices to share files, printers, and the internet. - Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
A MAN covers a city or large campus, linking multiple LANs for faster communication and data sharing. - Wide Area Network (WAN):
A WAN connects networks over long distances, often worldwide. The Internet is the largest WAN. - Wireless Networks:
Wireless networks like Wi-Fi or mobile networks connect devices without cables, making networking more flexible and convenient. - Virtual Private Network (VPN):
A VPN creates a secure network over the internet, protecting data and privacy while connecting devices remotely.
Network Devices
Network devices like routers, switches, hubs, modems, access points, and NICs help devices connect, communicate, and share data within a network or to the internet.”
- Router:
A router directs data between different networks, like your home network and the internet. - Switch:
A switch connects multiple devices within a LAN, allowing them to communicate efficiently. - Hub:
A hub is a basic device that links devices in a LAN. It is an older technology and less efficient than a switch. - Modem:
A modem connects your local network to the internet, translating signals between devices and your ISP. - Access Point:
An access point extends Wi-Fi coverage, letting wireless devices connect to the network. - Network Interface Card (NIC):
A NIC allows a device, like a computer or printer, to connect to a network via a wired or wireless connection.
Network Topologies
Network topologies show how devices in a network are connected and how data flows between them. Common types include star, bus, ring, mesh, and hybrid, each with its own setup and advantages.
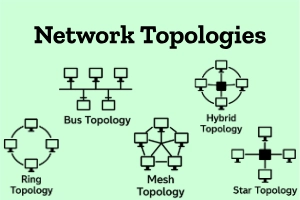
Here are some common types of network topologies.
- Bus Topology:
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single line. It is simple and cheap but less reliable because if the main line fails, the network stops working. - Star Topology:
In a star topology, all devices connect to a central hub or switch. It is easy to manage and troubleshoot, but if the hub fails, the network goes down. - Ring Topology:
In ring topology, devices are connected in a circular path. Data flows in one direction, making it orderly, but a break in the ring can disrupt the network. - Mesh Topology:
In mesh topology, devices are interconnected, offering high reliability and multiple paths for data. It is often used in critical networks. - Hybrid Topology:
Hybrid topology combines two or more topologies, taking advantage of their strengths while reducing weaknesses.
How Computer Networking Works?
Computer networking is how computers and devices connect to share data and communicate. It works using rules called protocols that guide how information is sent and received.
- Data Transmission: Information is broken into small packets that travel across the network.
- TCP/IP: Ensures data reaches the right device safely.
- HTTP: Lets you browse websites.
- FTP: Helps transfer files between computers.
- Wired: Uses cables for stable connections.
- Wireless: Uses Wi-Fi or Bluetooth for convenience.
- Real-life analogy: Mailing letters is like wired networks (slower but reliable), while instant messaging is like wireless networks (fast and flexible).
Advantages vs Disadvantages
A comparison table shows the advantages and disadvantages of a topic side by side for easy understanding. It helps quickly see the benefits and drawbacks at a glance.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to compare | May oversimplify details |
| Saves time | Can miss context |
| Highlights key points | Doesn’t show solutions |
| Helps decision-making | May be biased |
| Clear visual format | Limited space for explanation |
Examples of Computer Networks
Here are some real-life computer networking examples that you might use or see every day:
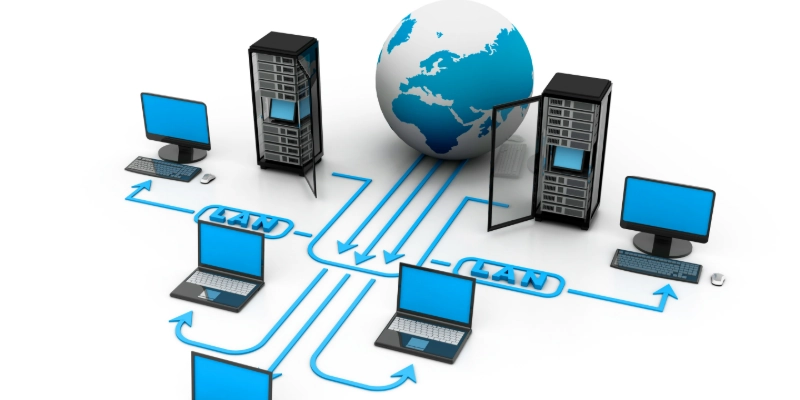

- Home Wi-Fi network: Connects your phones, laptops, and smart gadgets at home.
- School/college LAN: Links computers in classrooms or labs for sharing resources.
- Office LAN/WAN: Connects employees’ computers and sometimes links multiple office locations.
- Internet (global WAN): The largest network in the world, connecting millions of devices worldwide.
- Cloud networks (Google Drive, Dropbox): Store and share files over the internet, accessible from anywhere.
These examples of computer networks show how networking helps devices communicate and share data in different settings.
Future of Computer Networking
The future of computer networking is exciting, with many new technologies making networks faster, smarter, and more secure:
- Faster internet (5G, 6G): Speeds will increase, allowing instant downloads and smoother streaming.
- IoT integration: More smart devices will connect and communicate seamlessly.
- AI-driven networks: Artificial intelligence will manage and optimize networks automatically.
- More secure and scalable networks: Advanced security will protect data, and networks will grow easily as needed.
- Edge computing: Data processing will happen closer to devices, reducing delays and improving efficiency.
These next-generation networks will change how we use the internet and connected devices in daily life.
Conclusion
Computer networking connects devices so they can share information. Networks like LAN, WAN, and Wi-Fi use devices such as routers, switches, and computers. Networking helps in fast communication, file sharing, and collaboration, though it can have security risks. It is essential in daily life and business.
Computer networking is the backbone of modern communication and technology, making our connected world possible.
FAQs
Got more questions? Check out our FAQs to learn everything about computer networking!
Computer networks are systems that connect devices to share data and communicate. Common types include LAN, WAN, MAN, PAN, and wireless networks.
You can connect three computers using a router or switch with Ethernet cables, or via Wi-Fi if they support wireless networking. Then, make sure all computers are on the same network and share the same workgroup or network settings.
The main software components of a computer network are network operating systems, protocols (like TCP/IP), and network management tools. These help devices communicate, manage data, and maintain network security.
The basics of computer networking include connecting devices, sending data in packets, using protocols like TCP/IP, and choosing network types like LAN, WAN, or Wi-Fi. It also involves network devices such as routers, switches, and servers to manage communication.
Common software used for computer networking includes network operating systems (like Windows Server, Linux), protocol software (TCP/IP), network management tools (like Wireshark, SolarWinds), and file-sharing or communication applications. These help devices connect, share data, and monitor the network.
Software and networking serve different purposes, so one isn’t “better” than the other. Software runs applications and performs tasks on devices, while networking connects devices so they can share data and communicate. Both are essential and work together in modern computing.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks