Parts of a Mouse: Easy and Quick Notes
Published: 20 Oct 2025
Have you ever wondered what happens inside your mouse when you move it around or click on something? This tiny device may look simple, but it’s full of smart parts working together to control your computer.
A mouse is an input device that helps you give commands with just a small hand movement. The parts of mouse make it possible to move the pointer, click icons, and scroll through pages smoothly.
In this article, we’ll uncover all the secret parts of mouse and see how each one helps make your computer come alive!
What is a Computer Mouse?
A computer mouse is an input device that controls the movement of the pointer on a computer screen. It allows users to interact with the computer by moving, clicking, or selecting items. This simple tool plays a big role in how to use computers every day.
For example, when you click to open a folder, drag a file, or scroll through a webpage, you are using a mouse to send commands to the computer.
Main Parts of Mouse
A computer mouse may look small, but it has many important parts that work together to control your screen. Each part has its own job; some handle clicking, some track movement, and others help with scrolling.
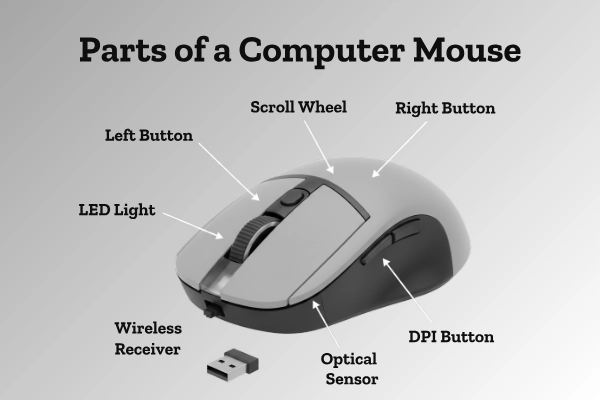
Understanding these parts helps you know how a mouse makes using a computer so simple and smooth. Every computer has some common parts of mouse that perform specific functions.
Let’s learn about them one by one.
- Left Button
- Right Button
- Scroll Wheel
- Mouse Ball
- Cable
- Wireless Receiver
- DPI Button
- LED Light
Let’s talk about them in detail.
Left Button
The left button of the mouse is the most used part. It is used for selecting, clicking, dragging, and opening files.
Example: When you click a link or open a program, you are using the left button.
Function: The function of the left mouse button is to act as the primary selection and activation tool.
Right Button
The right button of the mouse opens shortcut or context menus. It gives you quick access to options like copy, paste, or properties.
Example: When you right-click a file to rename it, you use the right button.
Function: The function of the right mouse button is to show context-specific menus.
Scroll Wheel
The scroll wheel of the mouse is located between the left and right buttons. It helps you scroll up or down on web pages and documents. Some scroll wheels can also be clicked to open links in new tabs.
Example: When you scroll through a long article or move up and down a Facebook feed, you are using the scroll wheel.
Function: The function of the scroll wheel is to help navigate pages quickly without using the scroll bar.
Mouse Ball
The sensor of the mouse detects movement on a surface. Older mice used a rubber ball, while modern ones use an optical or laser sensor. This sensor converts your hand movements into signals that the computer understands.
Example: When you move your mouse, and the pointer moves on the screen, the optical sensor in the mouse is doing its job.
Function: The optical sensor in the mouse tracks movement and controls the direction of the cursor.
Cable or Connector
In a wired mouse, the cable of the mouse connects it to the computer through a USB port. This cable sends data signals between the mouse and the computer.
Example: When you plug your wired mouse into the computer’s USB port and start using it instantly, that’s because of the mouse connector.
Function: The mouse connector transfers movement and click data to the system.
Wireless Receiver
A wireless mouse receiver is found in wireless models. It is a small USB device that connects the mouse to the computer using Bluetooth or RF signals.
Example: When you insert a small USB receiver into your laptop and move your wireless mouse without any cable, you are using the wireless mouse receiver.
Function: This part allows the mouse to work without physical cables, giving you more freedom of movement.
DPI Button (Optional)
The DPI button on the mouse is found in gaming or advanced mice. It changes the sensitivity or pointer speed.
Example: A higher DPI setting makes the cursor move faster on the screen.
Function: It controls mouse sensitivity and accuracy.
LED Light
The LED in the mouse is usually located underneath. It helps the optical sensor detect surface movement. In optical and laser mice, this light ensures smooth and accurate tracking.
Example: When you lift your mouse and see a red or blue light glowing under it, that’s the light under the mouse helping the sensor detect movement.
Function: The LED light in the mouse enables accurate motion detection and pointer movement.
| Part Name | Function | Example / Use |
| Left Button | Selects or opens files | Clicking a link |
| Right Button | Opens context menu | Copying or pasting |
| Scroll Wheel | Moves page up or down | Browsing a website |
| Optical Sensor / Ball | Detects movement | Moving cursor |
| Cable / Receiver | Moves the page up or down | USB or Bluetooth |
| DPI Button | Adjusts speed or sensitivity | Gaming mice |
| LED Light | Tracks surface motion | Found in optical mice |
Internal Parts of Mouse
Inside every computer mouse, several mouse hardware components work together to make it function smoothly. These hidden parts send signals, detect clicks, and control movement. Knowing the internal parts of mouse helps you understand how this small device performs big tasks every day.
Here are the main internal parts of mouse and their functions:
| Internal Part | Function |
| Circuit Board | Controls all mouse actions and signals. It acts as the brain of the mouse, managing every command you give. |
| Micro Switches | Detect clicks from the buttons and send quick signals to the computer. |
| Encoder Wheel / Sensor | Measures the direction and speed of mouse movement for smooth cursor control. |
| Battery (Wireless Mouse) | Provides power to the mouse, allowing it to work without cables. |
| Receiver Chip | Sends and receives wireless signals between the mouse and computer for communication. |
Types of Computer Mouse
Different types of mouse have different structures, sensors, and working methods. Each type is designed to make computer use easier based on the user’s needs. Some use light or lasers for movement, while others work wirelessly with batteries.
Here are the main types of computer mouse and their key features:
| Type | Key Parts / Features | Example |
| Mechanical Mouse | Uses a rubber ball to track movement. The ball rolls on a surface, and sensors detect its direction. | Old computer models |
| Optical Mouse | Uses an LED light and optical sensor to detect movement. It has no moving parts, making it smoother and more accurate. | Modern desktops |
| Laser Mouse | Uses a laser beam instead of an LED for high precision. Works well on many surfaces and is great for detailed work. | Gaming use |
| Wireless Mouse | Uses a small receiver and battery to connect with the computer through Bluetooth or RF signals. | Laptop users |
| Gaming Mouse | Has extra buttons, a DPI control, and special software for speed and performance. | Professional gamers |
The main difference between an optical vs mechanical mouse is that an optical mouse uses light for movement, while a mechanical mouse uses a rubber ball. Modern users prefer optical and wireless models for their comfort and speed.
How the Mouse Works?
Have you ever wondered how a mouse works when you move or click it? The working of a computer mouse is based on converting your hand movements into signals that the computer can understand. It’s a quick and smart process that happens in just a fraction of a second.
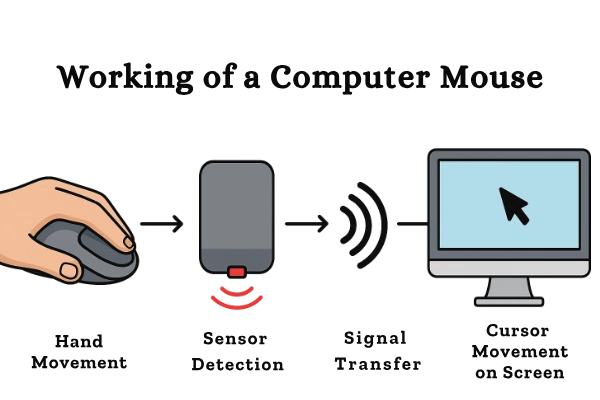
Here’s the mouse operation process in simple steps:
- You move or click the mouse.
The mouse senses your hand movement or button press. - The sensor or ball detects motion.
The optical sensor (or rubber ball in old mice) tracks how and where you move the mouse. - The signal is sent to the computer.
The internal circuit board and receiver send digital signals through a wire or wireless connection. - The cursor moves, or an action occurs on the screen.
The computer receives the signal and instantly moves the pointer or performs the click action.
Simple Example:
When you drag a file across your screen, the mouse converts your hand movement into digital signals. These signals tell the computer exactly where to move the file.
Importance of Mouse Parts
Every part of mouse plays an important role in its smooth functioning. If even one part stops working, the whole mouse may not function properly. Understanding the importance of mouse parts helps us know why each component is needed for the computer mouse functions we use every day.
- Without the left button: We cannot select, open, or click on items. It’s the main control for most actions on the screen.
- Without the sensor or ball: The pointer on the screen won’t move, making it impossible to control the cursor.
- Without the scroll wheel: Browsing long pages or documents becomes difficult and time-consuming.
- Without the cable or wireless receiver: No data can be sent between the mouse and the computer, so it won’t work at all.
- Without the LED light: The sensor cannot detect surface movement accurately.
Each part works together like a small team, making sure the mouse responds quickly and correctly to every move or click.
Maintenance Tips for the Mouse
To make your mouse last longer and work smoothly, you need to take good care of it. These simple mouse care tips will help you keep it clean, fast, and responsive.

Knowing how to maintain a computer mouse can also prevent common problems like slow movement or broken buttons.
- Keep the mouse clean and dust-free.
Wipe the surface regularly to remove dirt, especially around the buttons and scroll wheel. - Use it on a smooth surface or a mouse pad.
A flat surface helps the sensor detect movement correctly and prevents scratches. - Check batteries regularly (for wireless mice).
Low batteries can cause lag or connection issues, so replace them when needed. - Avoid dropping or pressing too hard.
Gentle use protects internal parts like sensors and micro switches from damage. - Update drivers if not working properly.
Sometimes the mouse may not respond well; updating its driver can fix many issues.
With these easy maintenance steps, your mouse will stay in good condition and perform smoothly for a long time.
Conclusion
From the click of a button to the glide of a cursor, every part of mouse works together to make computing easy for everyone. Each part has its own job that helps the mouse work smoothly and quickly.
Understanding the parts of mouse helps beginners know how a computer responds to their clicks and movements. Whether wired or wireless, the mouse is a simple yet powerful tool that makes using a computer easy and fun.
Keep clicking, keep learning, because every move counts in the world of computers!
FAQs
Before you go, let’s answer some common questions about the parts of mouse!
A computer mouse usually has about five to eight main parts, including buttons, a scroll wheel, and a sensor. The number can vary depending on the mouse type and design.
The main parts of mouse are the left button, right button, scroll wheel, optical sensor, and cable or receiver. Some advanced mice also have a DPI button and an LED light.
The sensor is the most important part of a mouse because it detects movement and controls the cursor on the screen. Without it, the mouse cannot function properly.
The middle part of a mouse is called the scroll wheel. It helps you move up and down on web pages or documents easily.
The clicking part of a mouse is called the mouse button. Most mice have a left button and a right button for different actions.
The clicking part of a mouse is called the mouse button. Most mice have a left button and a right button for different actions.
The scrolling part of a mouse is called the scroll wheel. It allows you to move up and down on web pages or documents smoothly.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks