Different Types of Memory Explained
Published: 2 Nov 2025
Have you ever wondered how your computer remembers everything you do? That’s because of its memory! Computer memory is the part that stores data, instructions, and information.
It helps the computer work fast and remember what you do. There are different types of memory in a computer. Each type has a special job, and they all work together to keep your computer quick and smart.
In this article, you’ll learn about all types of memory with simple examples, diagrams, and easy comparison tables.
What is Computer Memory?
Computer memory is a storage space that helps the computer store data, instructions, and information either temporarily or permanently.

It helps the computer remember what you do, just like our brain remembers information. Without memory, your computer wouldn’t know what task to do next.
Example: When you open a file or app, it’s loaded from storage into memory so your computer can work faster and respond quickly.
Why is Memory Important in a Computer?
Memory is very important for a computer’s smooth working. It helps the system store programs and data while processing them. Without memory, the CPU cannot perform tasks efficiently.
- Storage: Holds data and programs while the computer is running.
- Speed: Makes processing tasks faster and smoother.
- Support for CPU: Helps the processor perform actions correctly.
- Multitasking: Allows running many apps at the same time.
- Performance: Improves the overall performance of the computer system.
Faster memory also makes the computer run quickly and allows easy multitasking, like browsing while playing music.
Memory Hierarchy in Computers
Memory hierarchy means how different types of memory in a computer are arranged in levels based on their speed, size, and cost. This structure helps the computer work faster and store data efficiently.
| Level | Memory Type | Speed | Size | Cost |
| 1️⃣ | Registers | Fastest | Very small | Very high |
| 2️⃣ | Cache Memory | Very fast | Small | High |
| 3️⃣ | Primary Memory (RAM, ROM) | Fast | Medium | Moderate |
| 4️⃣ | Secondary Memory (Hard Disk, SSD) | Slower | Large | Low |
| 5️⃣ | External Memory (USB, CD, Cloud) | Slowest | Very large | Low |
At the top levels, memory is very fast but small and costly. As we move down, memory becomes slower but larger and cheaper. Together, these levels keep the computer balanced between speed and storage.
Major Types of Memory in a Computer
Computer memory plays a big role in how a computer works. It stores data, programs, and instructions that the CPU needs to perform tasks.

Mainly, computer memory is divided into two types: Primary Memory and Secondary Memory. Both work together to make the computer fast, reliable, and ready for use.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory is also called main memory because the computer uses it directly while working. It stores data that the CPU needs right now. This memory is fast, but it can hold only a limited amount of data.
It includes two main parts:
- RAM (Random Access Memory): It stores temporary data. When you switch off the computer, this data is lost.
- ROM (Read Only Memory): It stores permanent instructions, like how to start the computer when you press the power button.
Example: When you open a game, it loads into RAM so it can run quickly.
Secondary Memory (Storage Memory)
Secondary memory is used to store data permanently. It keeps your files, software, photos, and videos safe even when the computer is turned off. This memory is slower than primary memory but has much more storage space.
Common types of secondary memory include:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
- Solid State Drives (SSD)
- USB Drives and Memory Cards
- CDs, DVDs, and Cloud Storage
Example: When you save a file or photo, it is stored in your hard disk or SSD for future use.
Together, primary memory and secondary memory make the computer work smoothly; one helps it think fast, and the other helps it remember for long.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory is the main working area of a computer. It stores data and programs temporarily while they are being used. This memory allows the CPU to access information quickly and perform tasks efficiently.
Features:
Here are some features of primary memory.
- Fast: It is very quick and can be accessed directly by the CPU.
- Volatile: Data is lost when the power is turned off.
- Limited Size: It can store only a small amount of data compared to secondary memory.
Types of Primary Memory
Primary memory is divided into two main types: RAM and ROM.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM is a type of memory that stores data temporarily. When the computer is turned off, all data in RAM is erased. It helps the CPU process data fast, making the computer run smoothly.
There are two types of RAM:
| Type | Full Form | Use | Speed | Volatile |
| SRAM | Static RAM | Used as cache memory | Very fast | Yes |
| DRAM | Dynamic RAM | Used as the main system memory | Fast | Yes |
Example: When you open a browser or game, the data loads into RAM so your computer can access it quickly.
ROM (Read Only Memory)
ROM is a type of non-volatile memory, which means the data stays safe even when the power is off. It stores firmware and startup instructions that help the computer start and work properly.
| Type | Full Form | Description |
| PROM | Programmable ROM | Can be written only once |
| EPROM | Erasable PROM | Can be erased with UV light |
| EEPROM | Electrically Erasable PROM | Can be rewritten using electricity |
Examples: BIOS in computers, memory in embedded systems, and device firmware.
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a small, high-speed memory that sits between the CPU and RAM. It stores frequently used data and instructions, so the CPU can access them quickly without waiting for the main memory.
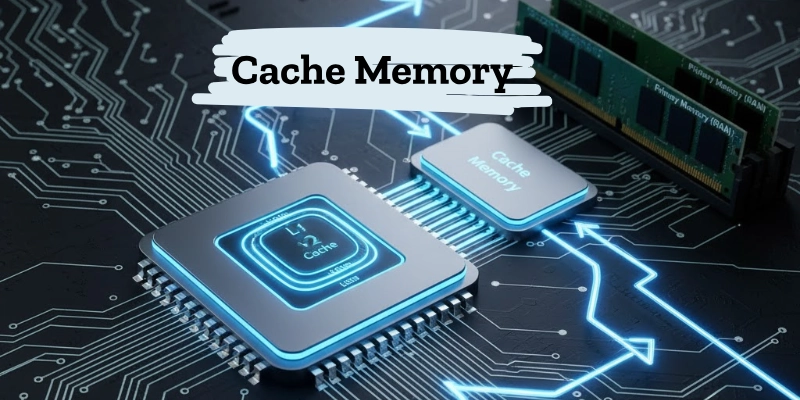
| Type | Location | Speed |
| L1 Cache | Inside CPU | Fastest |
| L2 Cache | Between CPU and RAM | Fast |
| L3 Cache | Shared by CPU cores | Moderate |
In simple words, cache memory works like a shortcut, helping your computer access important data much faster.
Register Memory
Register memory is the smallest and fastest type of memory in a computer. It is located inside the CPU and is used to hold data, instructions, or addresses that are currently being processed.
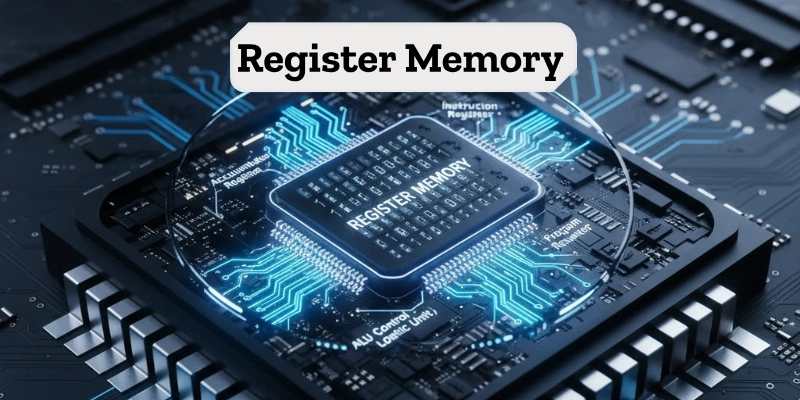
Registers work directly with the CPU, which makes them faster than all other types of memory. They help the processor complete tasks quickly by storing temporary values during operations.
Examples:
- Accumulator Register: Stores results of calculations.
- Instruction Register: Holds the current instruction being executed.
Although register memory is very fast, it is limited in size and can store only a small amount of data.
Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is a special type of memory created when the computer’s RAM is full. It uses a part of the hard drive or SSD as temporary memory to store extra data that doesn’t fit in the RAM.
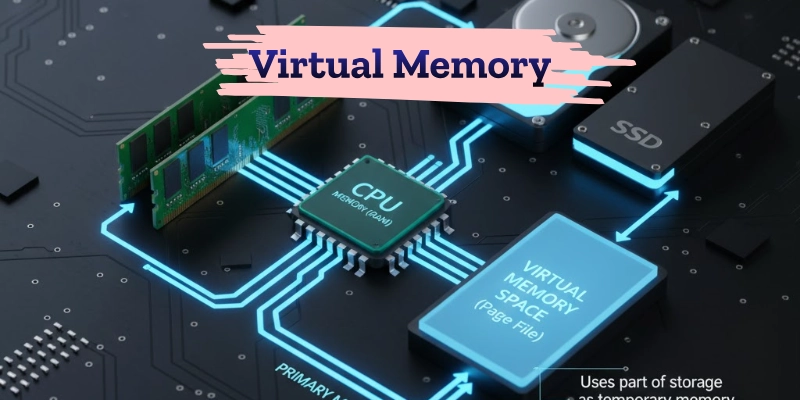
This helps the computer run more programs at the same time and prevents it from slowing down or crashing. However, virtual memory is slower than real RAM because the hard drive takes more time to read and write data.
In simple words, virtual memory acts like extra space that helps your computer multitask smoothly, even with limited RAM.
Volatile vs Non-Volatile Memory
Computer memory can be divided into two main types: volatile and non-volatile. The main difference between them is how they store data when power is turned off.
Volatile memory stores data temporarily and loses it when the computer is shut down. Non-volatile memory, on the other hand, keeps data permanently, even without power.
| Feature | Volatile Memory | Non-Volatile Memory |
| Data Storage | Temporary | Permanent |
| Power Off Effect | Lost | Retained |
| Example | RAM | ROM, HDD |
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Use | Processing | Storage |
Volatile memory is used for active work, while non-volatile memory is used for long-term storage.
Primary vs Secondary Memory
Computer memory is mainly divided into primary memory and secondary memory, and both play important but different roles.
Primary memory works directly with the CPU for quick processing, while secondary memory is used for long-term data storage.
Here’s a simple comparison:
| Feature | Primary Memory | Secondary Memory |
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Storage | Limited | Large |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Access | Direct (by CPU) | Indirect |
| Data Retention | Temporary | Permanent |
Primary memory (like RAM) helps in processing tasks quickly, while secondary memory (like a hard disk) helps in storing data permanently.
Characteristics of Computer Memory
Every type of computer memory has special features that decide how it works and how it affects the computer’s performance. These characteristics help us understand the speed, storage, and cost of different memories.
- Speed: Shows how fast data can be read or written. Faster memory helps the computer run smoothly.
- Capacity: Tells how much data the memory can store at one time.
- Volatility: Explains whether data stays safe after the power is turned off.
- Accessibility: Shows how easily the CPU can access stored data.
- Cost: Higher-speed memory usually costs more, while slower memory is cheaper.
Computer memory is chosen based on the right balance of speed, size, and cost for a system’s needs.
Importance of Memory in System Performance
Computer memory plays a major role in how fast and smoothly a system works. The more memory a computer has, the better it can handle multiple tasks at the same time.
Good memory helps the CPU process data quickly, reduces system load, and improves the speed of applications. It is especially important for gaming, graphic design, video editing, and other heavy tasks that need quick data access.
In simple words, more memory = smoother performance and a faster computer experience.
Conclusion
In this guide, we learned about the different types of computer memory, how they are organized in a hierarchy, and why they are so important for system performance.
Each type of memory, from registers and cache to RAM, ROM, and secondary storage, plays a special role in helping the computer work fast and efficiently. All these memories work together to make the computer powerful, reliable, and ready for multitasking.
Memory is like the heart of your computer; it keeps everything running smoothly and efficiently.
FAQs
Have more questions about computer memory? Let’s clear them up below!
Memory is the part of a computer that stores data and instructions. Its main types are primary, secondary, cache, register, and virtual memory.
The main types of main memory are RAM and ROM. They help the computer store and process data quickly.
Primary memory has two main types: RAM and ROM. RAM is temporary, while ROM stores data permanently.
Secondary memory includes hard drives, SSDs, CDs, DVDs, and USB drives. It stores data permanently for long-term use.
No, ROM is part of primary memory, not secondary. It stores the computer’s startup and system instructions.
RAM is faster because the CPU can read and write data directly from it. ROM is slower as it only allows reading fixed instructions.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks