What is a 3d Printer – Definition, Types & How Does it Work
Published: 5 Dec 2025
Imagine turning your ideas into real objects right on your desk; that is the magic of a 3D printer. Many people today wonder what is a 3D printer because it helps create things quickly, easily, and in many shapes.
Schools use it for projects, homes use it for toys and tools, labs use it for science models, and industries use it for machine and medical parts. It saves time, reduces cost, and turns creative ideas into real objects you can hold.
In this article, we will learned about what a 3d printer is, its types, uses, and features.
What Is a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer is a machine that can turn digital designs into real, physical objects. It works by adding material layer by layer, building the object from the bottom up. This process is called 3D printing, and it allows people to create items in different shapes and sizes quickly and easily.

For example, you can print a small toy, a phone stand, or even parts for machines using a 3D printer.
Here are some key points about 3D printers:
- Layer-by-layer printing: The printer builds objects one thin layer at a time.
- Digital designs: Objects are made from designs created on a computer.
- Versatile materials: 3D printers can use plastic, metal, resin, and other materials.
- Custom objects: You can make unique or custom items easily.
- Time-saving: Complex items that take hours or days by hand can be printed faster.
How Does a 3D Printer Work?
A 3D printer turns digital designs into real objects by carefully building them layer by layer. It may sound complicated, but the process is simple and easy to follow.
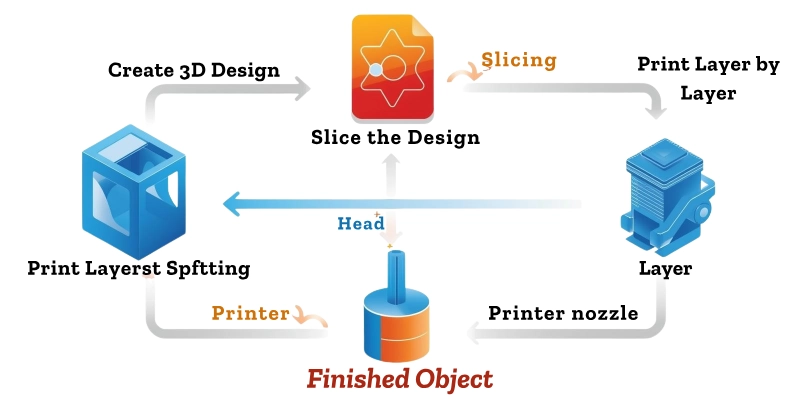
- Create a 3D Design: First, you design the object using special software. This can be anything from a small toy to a phone stand.
- Slice the design: The design is then “sliced” into thin layers using slicing software. These layers tell the printer how to build the object step by step.
- Print layer by layer: Finally, the 3D printer adds material layer by layer, following the sliced design, until the object is complete.
This process allows anyone to turn ideas on a screen into real, usable objects.
Example: If you want a small toy car, you first design it on the computer, slice it into layers, and then the 3D printer builds it layer by layer into a real toy car you can hold.
Types of 3D Printers
3D printers come in different types, each designed for specific tasks and materials. Choosing the right type depends on what you want to print, the level of detail, and the material you plan to use.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM is the most popular type of 3D printer used by beginners and professionals alike. It is easy to use and works well for creating everyday objects, prototypes, and simple designs.
- The most common type of 3D printer.
- Uses plastic filament that melts and is deposited layer by layer to build objects.
SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA printers are known for their high precision and smooth finishes. They are often used when detailed and small objects are needed, like jewelry, models, or dental tools.
- Uses liquid resin that hardens when exposed to a special light.
- Great for making very detailed and smooth objects.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS printers are used for strong and durable objects. They are popular in industries where functional parts are needed, like automotive or aerospace components.
- Uses powdered material like plastic, metal, or ceramic.
- A laser fuses the powder layer by layer to make strong objects.
Other Types
There are also specialized 3D printers for unique purposes. Some can print metal parts, while others can even create food items layer by layer.
- Metal 3D Printers: Print parts using metal powder or wire.
- Food 3D Printers: Can print chocolate, dough, or other edible items layer by layer.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
3D printers can use many types of materials depending on what you want to make. Here are some common materials and their uses:

- PLA: A popular plastic used for toys, models, and simple objects.
- ABS: Strong plastic used for durable parts and functional objects.
- Resin: A liquid material used for detailed and smooth models like jewelry or miniatures.
- Nylon: A flexible and strong material used for mechanical parts and tools.
- Metal powder: Used to print metal parts for machines, cars, and industrial tools.
- Food materials (chocolate, dough): Used to create edible items like custom chocolates or cakes.
Benefits of Using a 3D Printer
3D printing makes creating objects faster, cheaper, and easier. It is useful for students, hobbyists, and industries to turn ideas into real items quickly.
- Faster Prototyping: Print designs quickly, test, and modify them.
- Cost-Effective: Uses less material and avoids expensive molds.
- Customization: Make personalized or unique objects easily.
- Less Waste: Uses only the material needed and reduces leftovers.
- Easy Learning Tool: Helps students learn with hands-on models and encourages creativity.
Limitations of 3D Printers
While 3D printing is amazing, it has some limitations that beginners and industries should know. It is not perfect for every task and can have challenges depending on the size, material, and type of project.
- Slow for Large Jobs: Printing big objects can take many hours or even days.
- Material Limits: Only certain plastics, resins, metals, or food items can be used.
- Surface Finish Issues: Some 3D printed objects may need extra work to look smooth.
- Requires Training: Beginners need time to learn software and printer settings.
- Expensive for Big Projects: Large or complex items can cost a lot in materials and time.
Real-Life Uses of 3D Printers
3D printers are used in many areas of life, from education to industry. They help people create objects faster, cheaper, and with more flexibility.

Here are some real-life uses of 3d printers.
- Schools and Colleges: For student projects, models, and learning tools.
- Home Projects: Make toys, tools, and custom household items.
- Medical Field: Print prosthetics, implants, and surgical models.
- Construction: Build small-scale models and even parts of buildings.
- Automotive Industry: Make car parts, prototypes, and custom components.
- Fashion and Jewelry: Create unique designs, accessories, and detailed models.
- Aerospace: Print plane parts, drones, and lightweight components.
- Food Industry: Print chocolates, cakes, and other edible creations.
3D Printer Types Comparison
This table compares the main 3D printer types: FDM, SLA, and SLS. It shows differences in cost, print quality, materials used, and how easy each printer is to use. Beginners can quickly see which type fits their needs.
| Type | Cost | Quality | Material | Ease of Use |
| FDM | Low | Medium | Plastic filament | Easy |
| SLA | Medium | High | Resin | Medium |
| SLS | High | High | Powder (plastic, metal) | Hard |
3D Printing vs Traditional Manufacturing
This table highlights how 3D printing differs from traditional manufacturing methods. It compares speed, cost, material waste, customization options, and materials, showing why 3D printing is often faster and more flexible for small projects.
| Feature | 3D Printing | Traditional Manufacturing |
| Speed | Fast for small batches | Fast for large batches |
| Cost | Low for small runs | High setup cost |
| Waste | Less | More |
| Customization | Easy | Hard |
| Materials | Limited | Wide range |
FDM Materials Comparison
This table compares common FDM materials like PLA, ABS, and PETG. It shows their strength, flexibility, and heat resistance, helping beginners choose the right material for their projects.
| Material | Strength | Flexibility | Heat Resistance |
| PLA | Medium | Low | Low |
| ABS | High | Medium | Medium |
| PETG | High | High | High |
Safety Tips for 3D Printing
3D printing is fun, but it’s important to stay safe while using the printer. Following simple precautions can prevent accidents and keep your workspace safe.

Here are some safety tips for 3d printing.
- Proper Ventilation: Always use the printer in a well-ventilated area to avoid fumes.
- Avoid Touching Hot Nozzle: Never touch the nozzle or heated bed during printing.
- Use Gloves When Handling Resin: Resin can be harmful to skin, so wear gloves.
- Keep Printer on a Stable Surface: Place the printer on a flat, steady surface to avoid tipping.
- Supervise Prints: Never leave the printer unattended while it is running.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about what is a 3D printer and how it turns ideas into real objects. 3D printers are used in schools, homes, industries, and even the medical and food fields, making creativity faster and easier.
Despite some limits, their ability to customize, save time, and inspire innovation makes them truly amazing.
With a 3D printer, your imagination is the only limit. Start creating and watch your ideas come to life!
FAQs
Don’t stop here, dive into the FAQs and take your 3D printing skills to the next level!
No, 3D printers don’t use traditional ink. They use materials like plastic filament, resin, or metal powder. These materials are melted or hardened layer by layer to build objects.
People use 3D printers to create objects quickly and easily. They are helpful for prototypes, custom items, and educational projects. They save time and allow creative designs that are hard to make by hand.
Objects made from certain materials, like glass or very soft fabric, cannot be printed. Large-scale construction without specialized printers is difficult. Complex electronics also can’t be fully printed.
They are widely used in schools, homes, labs, and industries. The medical and food sectors also use 3D printers. Basically, anywhere prototyping or custom objects are needed.
Risks include burns from hot nozzles or heated beds. Some resins and fumes can be harmful if not handled properly. Poor handling can also damage the printer or printed objects.
Some types, like SLA and SLS, use lasers to harden resin or fuse powder. FDM printers do not use lasers. The laser helps create precise and detailed objects.
It can be eco-friendly because it uses only the material needed. Some printers use recycled plastics. However, energy use and certain resins can still have environmental impacts.
Yes, some plastic filaments can be recycled and reused. It may require special equipment to reshape them. Not all printed plastic is easily reusable.
Custom products like jewelry, toys, and prototypes are highly profitable. Niche items for businesses or medical tools can also earn well. The value depends on demand and uniqueness.
No, a 3D printer cannot fully print itself. Some parts can be printed, but many essential components need to be manufactured separately. Assembly and electronics must be added manually.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks